Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is responsible for fighting infections in the body. It occurs when white blood cells, called lymphocytes, grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming tumors.
The lymphatic system consists of lymph nodes, spleen, thymus gland and bone marrow. All these areas are affected by lymphoma besides other organs throughout the body.
Different types of lymphoma are there, among which primary subtypes are:
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma – type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system
- Non- Hodgkin’s lymphoma – group of cancers that also affect the lymphatic system, but are more common and have a wider range of subtypes.
The type and severity of lymphoma will determine the best treatment options for an individual. Chemotherapy, immunotherapy medications, radiation therapy, bone marrow transplant or few combinations of these might be possible treatment options for lymphoma.
The different types of lymphoma apart from the primary subtypes are Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, cutaneous B-cell lymphoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Walden Strom macroglobulinemia.
Signs and Symptoms

Signs and symptoms related to lymphoma are:
- Painless swelling of lymph nodes in your neck, armpits or groin
- Persistent fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Shortness of breath
- Unexplained weight loss
- Itchy skin
Diagnosis
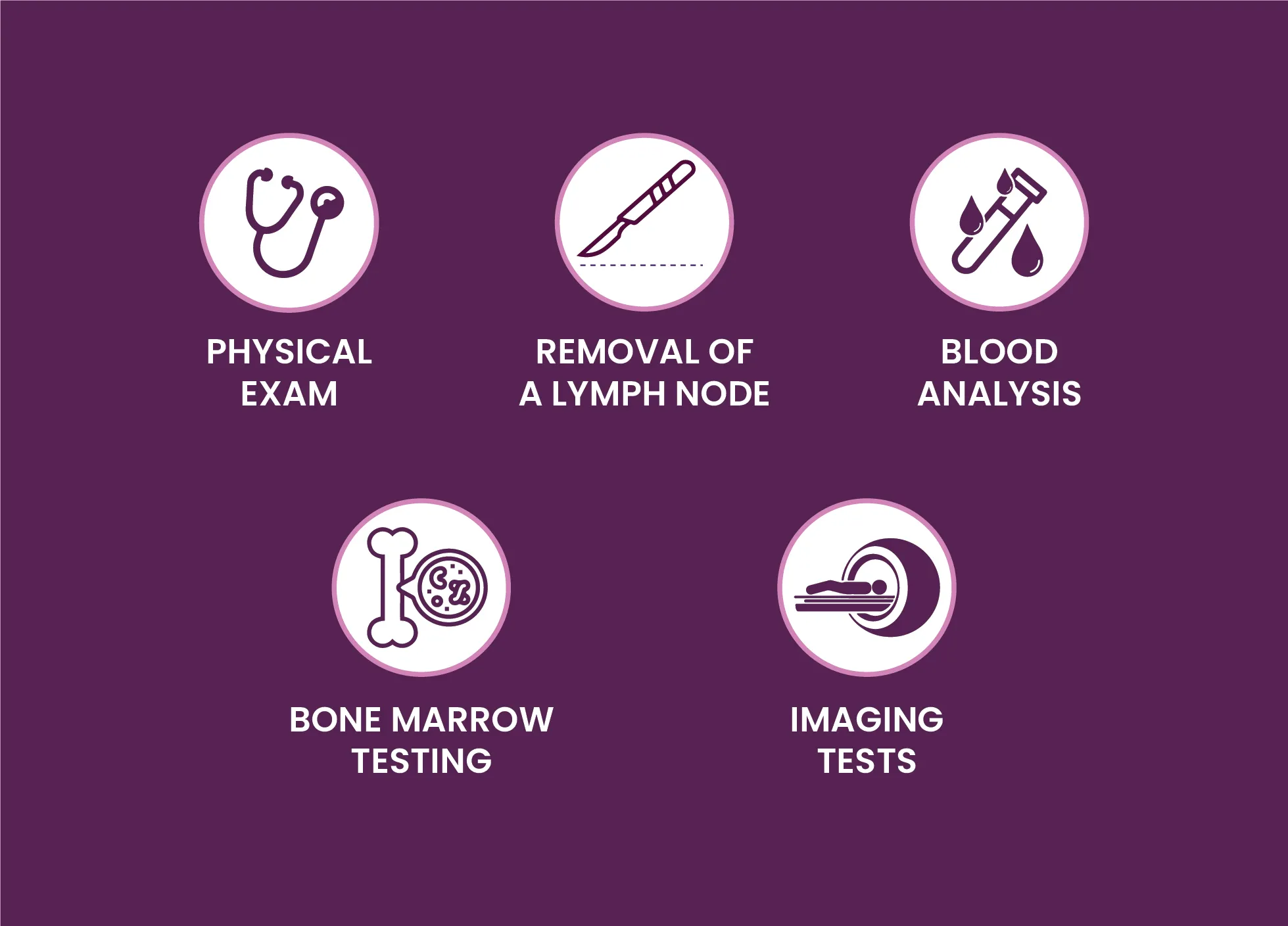
Diagnostic tests and procedures include:
- Physical examination: The doctor might check for any swollen lymph nodes, in your neck, underarm or groin, and swollen spleen or liver.
- Removal of a lymph node for testing: A lymph node biopsy may be recommended by your physician to either remove all or part of a lymph node for testing purposes. In addition to this, advanced tests are also performed to identify if lymphoma cells are present and what types of cells are involved.
- Blood Analysis: Number of cells in blood sample can help in proper diagnosis of the disease.
- Removing a sample of bone marrow for testing: Sample of bone marrow is removed by inserting a needle into your hipbone. The collected sample is analyzed for lymphoma cells.
- Imaging tests: To check for signs of lymphoma in different regions of your body, doctor might recommend imaging tests such as CT scan, MRI and PET.
Treatment

The right treatment choice for lymphoma depends largely on the type and stage of your disease, overall health and your preferences. The main aim of the treatment is to kill as many cancer cells and bring the disease into remission.
Various treatments available for lymphoma are:
- Active surveillance: Some varieties of lymphoma progress very slowly. When the signs and symptoms start interfering with the regular activities, your doctor might then start the treatment, till then to keep an eye on your health, you might conduct testing on a regular basis.
- Chemotherapy: The use of drugs to kill rapidly Proliferating cells, also known as cancer cells is called as chemotherapy. The drugs can either be administered into a vein or can be taken orally as a pill, depending on the specific type of drug prescribed.
- Radiation Therapy: High powered beams of energy, like X-ray and photons are used in radiation therapy to terminate the growth of cancer cells.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: Bone marrow transplant is also called as stem cell transplant which uses the high doses of chemotherapy and radiation to suppress your bone marrow. Once the healthy bone marrow stem cells are obtained either from your body or from a donor, it is then infused into your blood where they reach bones and reconstruct your bone marrow.
- Other treatments: Targeted drugs that usually target particular abnormalities in your cancer cells are the additional type of treatments used for lymphoma. Drugs used to destroy cancer cells with the aid of immune system is known as immunotherapy. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell therapy is a specialized treatment that employs body’s immune system’s T cell to eliminate cancer by genetically altering them to do so.
